Protocols
Perfusion of mice prior to freezing and processing for use in histologic methods and Microscopy
https://www.usf.edu/research-innovation/comparative-medicine/documents/training/perfusion.pdf
2020 Help with harvesting organs
2020_Help_For_mouse_necropsy.docx
Method to remove Brain and spinal cord:
https://doi.org/10.1038/laban0211-53
Perfusion fixation:
- Setup perfusion apparatus using a perfusion pump, and connect plastic small gauge tubes to a butterfly needle (30 gauge), and make sure all flow is occurring as expected, with saline or phosphate buffered saline.
- Place mouse under deep anesthesia following approved institutional protocols.
- Dissect open skin of the chest (V shape), and using scissors already primed for bone cutting, cut on either side of the chest, through the ribs to expose the heart and lungs
- Make a cut into the right atrium, which may be removed.
- Insert the butterfly needle into the left ventricle, and stabilize.
- Allow 5-20 ml of saline to enter the left ventricle, and watch to see the liver become bloodless, followed by the kidneys.
- Change the perfusate to an appropriate fixative let this perfuse the animal for about 15 minutes, until the body becomes stiff.
- Dissect away the required organs.
- Perfuse the lungs again via the trachea until all lobes are filled with fixative. Separate out each lobe and places in clearly labeled cassettes for processing into paraffin blocks
- All organs may now be processed into paraffin blocks for sectioning at room temperature, using the microtome
For Frozen sections:
- After fixation place in 15% sucrose in PBS for 24h.
- Replace sucrose with 20% (or) again 15% until tissue sinks (24h usually)
- Remove tissue from sucrose, blot off any excess and place in mold. This is an important step to avoid a "shell" of sucrose which coats the tissue and slows the freezing process.
NOTE: Sometimes 30% makes the tissue stickier and that 20% will give good results
- Transfer tissues to OCT (Optimum cutting temperature compound) chamber and surround with OCT
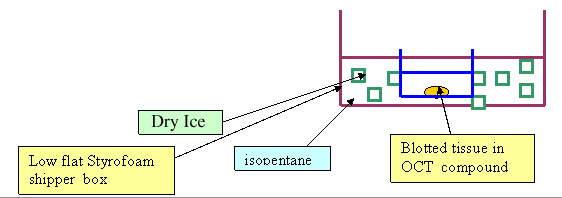
- Place mold in styrofoam container which holds dry ice/2-methyl butane slurry, and allow the block to freeze --until the OCT becomes white and is solid
- Remove and place on dry ice for an additional 15-30 minutes
- Store in labeled bags at minus 80 until required and process for frozen sections using the Cryostat.
TO FREEZE TISSUES OPTIMALLY, FOR FROZEN SECTIONING: see diagram below
- To inflate lungs before freezing: Make 1:1 OCT: PBS for tracheal infiltration to inflate lungs before freezing
- Get bench area ready with absorbent material, styrofoam board and dissection equipment
- Make freezing mixture: In a small styrofoam flat container, make a slurry with small bits of dry ice and 2 methyl butane. This will be the freezing mixture which will freeze the organs in OCT for frozen sections
- Lay euthanized animal on dissecting board
- To optimally examine brain, plan to perfuse animal with fixative, first with PBS, to deplete all of the blood, and then perfuse with freshly made 4% paraformaldehyde, to fix all the organs. If the fixed tissues are to be frozen for use in immunohistology assays, after fixation, they MUST be immersed in 30% sucrose in PBS at 4 degrees, until they sink, in order to cryoprotect and prevent freeze artefact and loss of tissue architecture.
- Expose trachea and infiltrate lungs with OCT/PBS mixture. Remove entire block and place on paper towel to drain before freezing in vinyl mold surrounded with OCT.
- Harvest tissues and place in sequence onto paper towels to dry off tissue fluids before placing into vinyl molds, FLAT ON THE BOTTOM OF THE MOLD to keep tissues all at the same level, and then fill with OCT.
- Spleen/thymus, lymph nodes. adrenals.
- Liver, pancreas, kidney, heart.
- OCT inflated and drained lungs.
- GI (small intestine, colon, ? stomach) and GU (Bladder, prostate, testis, ovary, uterus)
- Skin, skeletal muscle, salivary glands, mammary glands, (decalcified femur for blocks)
- Brain (dorsal surface down at bottom of mold)
- Place plastic molds containing organs and OCT into dry ice/ isopentane slurry till OCT turns white
- Remove plastic molds with frozen organs from dry ice/ 2 methyl butane and let them sit for a minute or so on paper towels, snap off the plastic molds and place frozen blocks into labeled bags for storage in labeled boxes in the second container of dry ice for storage at minus 70.
SUPPLIES:
- OCT Compound:� VWR Cat No: 25608-930
- Vinyl molds: Crymolds: Simport Scientific Catalog M475-3 or 80872-490
- Frozen sample write-on bags: VWR� Cat. No: 01-002-37
- 2-methyl butane (isopentane) Fisher Cat No: 03551-4
TO FIX FOR PROCESSING INTO PARAFFIN BLOCKS
see "histopathology" section for details
- Place THINLY sliced organs into well labeled plastic cassettes (see"histopathology" section for catalog numbers), snap shut and immerse into 10 volumes of fixative (10% buffered formalin).
- Skin, Spleen, Pancreas, Thymus SHOULD BE FLATTENED between two pieces of sponge, BEFORE fixing, to ensure the correct orientation when it is time to embed into paraffin wax, and to ensure flat sections.
- Let the organs fix for at least 24 hours (may go longer)
- Use Zinc containing fixatives or alcohol, if there is a need for immunohistochemsitry. INFORM THE CORE LAB OF THE DIFFERENT FIXATIVE THAT WAS USED or else the tissue will become too hard for sectioning if it stays in alcohol for days.
- Deliver to Core lab for processing into paraffin blocks
|
